HEAD AND CERVICAL SPINE
Similar to the cervical vertebrae, the cervical nerves are number from C1-C8. The cervical nerve follows the number of the vertebrae below it, with the exception of C8. The nerves roots break off into seperate branches which then innervate the muscles or stimulate the skin.
The vasculature of the cervical spine includes the cartoid arteries and jugular veins. These blood vessels are vital in supplying the brain and head with sufficient nutrients to carry out basic activities.



Cervical Nerves


Cervical Plexus (C1-C4)
The Cervical Plexus consists of the first four nerves of the cervical nerves. The superficial braches of the nerves innverate the skin and superficial surfaces of the head, neck and shoulder while the deep braches of the nerves innervate the muscles in the anterior neck and the diaphragm. The components of the deep branches of the cervical plexus:
-
Cutaneous: Lesser occipital, greater auricular, transverse cervical and supraclavicular
-
Ansa cervicalis: Infrahyoid and geniohyoid muscles
-
Phrenic: Diaphragm
-
Contributions to the Accessory Nerve: Sternocleidomastoid, Trapezius
-
Direct muscular Branches: Prevertebral muscles in neck.
The superficial branches of the Cervical Plexus:
-
Lesser Occipital nerve (C2): the skin posterior to the ear.
-
Great Auricular nerve (C2-C3): the ear and angle of the mandible to the mastoid process
-
Transverse Cervical nerve (C2-C3): the anterior neck
-
Supraclavicular nerve (C3-C4): the area over the clavical and shoulder
Brachial Plexus (C5-T1)
The Brachial Plexus consists of the last four cervical nerves and the first throacic nerve. The brachial plexus is broken down into different segments as it progresses:
-
3 Trunks: Superior (C5, C6), Middle (C7), and Inferior (C8,T1)
-
6 Divisions: Anterior(superior, middle and inferior), and Posterior (superior, middle, and inferior)
-
3 Cords: Lateral (Anterior divisions of the superior and middle trunk), Medial (Anterior division of the inferior trunk), Posterior (Posterior divisions of all three trunks)
The cord segements of the nerves break off into 5 terminal branches that innervate the muscles of the upper extremities:
-
Musculocutaneous (C5-C7): coracobrachialis, biceps brachii and brachialis along with the skin tot eh lateral forearm
-
Axillary (C5-C6): Shoulder joint and lateral skin over the deltoid
-
Median (C6-C7, C8-T1): muscles of the anteroir forearm and the tenar half of muscles and skin of palm
-
Radial (C5-T1): muscles of the posterior compartments of the arm and forearm and most the posterior skin of the upper extremity
-
Ulnar (C7-T1): forearm and hand medial to the midpoint of the fourth digit
Dermatomes and Myotomes
C1
-
Upper Trapezius
-
Middle Trapezius
-
Lower Trapezius
-
Longus Capitis
-
Rectus capitis Anterior
-
Obliquus Capitis Superior
-
Rectus Capitis Posterior Major
-
Rectus Capitis Posterior Minor
-
Semispinalis Capitis
C2
-
Upper Trapezius
-
Middle Trapezius
-
Lower Trapezius
-
Longus Capitis
-
Longus Colli
-
Rectus Capitis Anterior
-
Sterncleidomastoid
-
Semispinalis Capitis
C3
-
Upper Trapezius
-
Middle Trapezius
-
Lower Trapezius
-
Longus Capitis
-
Longus Colli
-
Levator Scapulae
-
Sternocleidomastoid
-
Semispinalis Capitis
C4
-
Upper Trapezius
-
Middle Trapezius
-
Lower Trapezius
-
Longus Colli
-
Iliocostalis Cervicis
-
Levator Scapulae
-
Sternocleidomastoid
C5
-
Upper Trapezius
-
Middle Trapezius
-
Lower Trapezius
-
Longus Colli
-
Iliocostalis Cervicis
-
Levator Scapulae
-
Rhomboideus Major
-
Serratus Anterior
-
Teres Major
-
Deltoid
-
Supraspinatus
-
Pectoralis Major
-
Subscapularis
-
Infraspinatus
-
Teres Minor
-
Biceps Brachii
-
Brachialis
-
Brachioradialis
-
Anterior scalene
-
Semipinalis Capitis
-
Semispinalis Cervicis
C6
-
Serratus Anterior
-
Coracobrachialis
-
Latissimus Dorsi
-
Deltoid
-
Teres Major
-
Pectoralis Major
-
Subscapularis
-
Infraspinatus
-
Biceps Brachii
-
Brachialis
-
Brachioradialis
-
Supinator
-
Pronator Teres
-
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus/Brevis
-
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
-
Extensor Digitorum
-
Extensor Indicis
-
Extensor digiti minimi
-
Extensor Pollicis Longus/Brevis
-
Abductor Pollicis longus
-
Longus Colli
-
Anterior Scalene
-
iliocostalis Cervicis
-
Semispinalis Capitis
C7
-
Serratus Anterior
-
Coracobrachialis
-
Latissimus Dorsi
-
Pectoralis Major
-
Triceps Brachii
-
Anconeus
-
Pronator Teres
-
Flexor Carpi Radialis
-
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus/Brevis
-
Extesnor Carpi Ulnaris
-
Flexor Digitorum
-
Extensor Digitorum
-
Extesnor Indicis
-
Extensor digiti minimi
-
Extensor Pollicis Longus/Brevis
-
Abductor Pollicis longus
-
Semispinalis Cervicis
C8
-
Latissimus Dorsi
-
Pectoralis Major
-
Triceps Brachii
-
Anconeus
-
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
-
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
-
Lumbricals
-
Palmer Interossei
-
Dorsal Interossei
-
Flexor Digitorum Superficialis/Profundus
-
Extensor Digitorum
-
Extesnor Indicis
-
Extensor digiti minimi
-
Abductor digiti minimi
-
Flexor Pollicis Longus/Brevis
-
Extensor Pollicis Longus
-
Abductor Pollicis longus
-
Adductor Pollicis
-
Opponens Pollicis
-
Semispinalis Cervicis
Cervical Vasculature

The cervical spine contains many vital blood vessels for the head and brain.
Arteries
-
Subclavian artery (2)
-
Common Cartoid artery (2)
-
External Cartoid artery (2)
-
Internal Cartoid artery (2)
-
Dorsal Scapular artery (2)
-
Suprascapular artery (2)
-
Verterbral artery (2)
Veins
-
Subclavian vein (2)
-
External Jugular vein (2)
-
Internal Jugular vein (2)
-
Brachiocephalic vein (2)
-
Inferior Thryoid vein (2)
-
Anterior Jugular vein (2)
Pulse
Cartoid pulse: Strongest pulse in the body. Place two fingers just lateral to the trachea on the anterior neck at the base of the chin.
Retrieved Novemeber: 14th 2-14 from: http://www.kryski.com
Retrieved Novemeber 14th 2014 from: http://www.cleaverspine.com
Retrieved Novemeber 14th 2014 from: http://www.cardiovascularcausesoftheshoulderpa.com
Retrieved Novemeber 14th 2014 from: http://www.doctorstock-photoshelter.com
Retrieved Novemeber 14th 2014 from: http://www.http://youtu.be/xGz0dZ2q1WM
Retrieved Novemeber 14th 2014 from: http://www.medical-dictionary.thegreendictionary.com
Retrieved Novemeber 14th 2014 from: http://www.dentistryandmedicine.blogspot.gif
Vertebral Artery Compression Syndrome
-
The vertebral arteries in the neck are compressed due to injury or blockage.
-
MOI: A direct blow to the neck resulting in compression from the vertebra or blockage of the artery from plaque build-up.
-
S/S: Decrease blood flow when the person turns their head, dizziness, rapid movement of the eyes called nystagmus, and possibly sudden loss of consciousness. Symptoms worsen when the blockage increases.
-
Treatment: Drug therapy with vascular drugs to improve blood flow and anticoagulants that thin the blood and allow it to move freely.
-
Diagnostic Tools: An MRI is a typically diagnosic tool used to identify a blockage in an artery. X-ray or CT scan can be used to determine or rule out other symptoms of vertebral artery compression syndrome.
-
Effect on Athletic Performance: Athletes with vertebral artery compression syndrome should not participate in high contact sports if it is caused by an injury. Light exercises while monitored are good to keep the body healthy along with a good diet.

Retrieved Novemeber 14th 2014 from: http://www.aao.org
Cervical Stenosis
-
The spinal canal is too small for the spinal cord and nerve roots, causing damage to the spinal cord or pinching the nerve roots.
-
MOI: Caused by shorter pedicles, degenerative arthritis, increase in size of the ligamentum flavum, and rheumatoid arthritis.
-
S/S: Neck pain, arm pain, and an electrical sensation that shoots down the back. Numbness in the arms and weakness may also occur.
-
Treatment: Surgery is usually necessary to correct the problem .Anterior cervical fusion and posterior laminectomy is the two basic types of surgery used to correct the problem.
-
Diagnostic Tools: Special tests. X-rays and CT scans can also locate the damage.
-
Effect on Athletic Performance: Athletes with cervical stenosis should not participate until cleared by a doctor, since surgery is necessary.

Retrieved Novemeber 14th 2014 from: http//:www.spineview.com
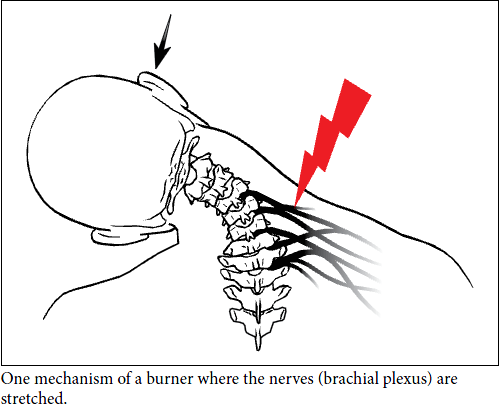
Burner/Stinger
-
A nerve in the brachial plexus that is compressed or stretched that results in a painful sensation in the neck. Can be felt throughout the affected arm, down to the fingers as a burning sensation.
-
MOI: Direct trauma to the cervical neck can cause compression of the vertebra or the clavicle in which the brachial plexus passes beneath. When a direct blow is delivered to this area, the shoulder is driven down and the neck is bent toward the other side.
-
S/S: Weakness in the affected shoulder’s arm. The muscle will try to lift the arm away from the body to do common movements. Tingling and a burning or stinging sensation gin the arm and hand are also common.
-
Treatment: PRICE method in the first 48 hours. Isometric exercises to increase the strength in the neck muscles as well as the arm and wrist is also done.
-
Diagnostic Tools: Special tests such as the Compression test and Spurling’s test are often done to test for a burner or stinger by recreating the MOI. Cervical distraction can relieve the pain.
-
Removal from participate due to possible repetitive trauma that can lead to nerve damage in the brachial plexus.
Retrieved Novemeber 14th 2014 from: http//:www.healthychildren.org
Information retrieved from:
Biel, A, (2012). Trail Guide to the Body. A.B. Boulder, CO: Books of Discovery
Krali, J. (2013). Head Injury Notebook. Retrieved November 14th, 2014.