HEAD AND CERVICAL SPINE
Mouth, Teeth, and Oral Cavity
Mouth
-
Tongue: Used for tasting, speech, forming food into a bollus and moving it to the back of the mouth to be swallowed.
-
Soft Palate and Uvula: used to close off the nasopharynx pathway when swallowing
-
Hard Palate: directs food to the back of the throat, assists in speech
-
Palatine Tonsil: lymphatic tissue
-
Lips: food intake, speech articulation, facial expression
Teeth
-
Used for chewing and provides point for tongue to push against during speech.
-
28 teeth total in grown adults
-
Incisors (4 upper, 4 lower): four most anterior teeth, used for cutting food
-
Cuspids (2 upper, 2 lower): tearing food
-
Bicuspids (2 upper, 2 lower): also called premolars, crushing and grinding food
-
Molars (6 upper, 6 lower): crushing and grinding food
-
-
Three main parts to the tooth: crown, neck, root
Assessment
-
Observation
-
Check for bleeding, ecchymosis, discoloration (white, yellow, blue, etc.)
-
Look for obvious deformity, chips, or missing teeth and have patient look in a mirror (they know themselves best!)
-
Check gums for pinkness, discoloration, swelling, or bleeding
-
Tongue Depressor, Pen Lights, and mirrors are useful tools during examinations
-
-
Annual Dental Examination
-
Patients should have teeth cleaned once a year by a professional
-

(http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/395124/mout) Retrieved Nov 11 2014

(http://www.webmd.com/oral-health/picture-of-the-teeth) Retrieved Nov 11 2014
Tooth Extrusion
-
Partial displacement of a tooth inferiorly (partially pulled out); caused by direct blow to the mouth.
-
Symptoms - pain, bleeding, temperature sensitivity, elongated appearance of affected tooth
-
Diagnosis - visual observation
-
Treatment - immediate referral to a dentist, who will reposition and splint tooth in place
-
Prevention - mouth guards and facial protection such as masks or cages
-
Athlete should rest a few days prior to return to play, then may participate as tolerated.
&contentUrl=srg/98/01-Diagnosis/with-displacement.jsp/)
Retrieved Nov 13 2014
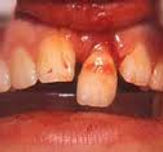
Tooth Fracture
-
Fracture of the tooth; caused by direct trauma.
-
Symptoms - pain, missing or displaced tooth, bleeding, swelling.
-
Diagnosis - visual examination, Ellis Classification
-
Treatment - Immediate referral to dentist; take any displaced pieces you can find and put them in a solution of tooth saver or in milk and bring along to the dentist. Artificial teeth may be used to replaced fracture or missing teeth.
-
Prevention - mouth guards
-
Athlete can participate as tolerated, but should rest after any procedure to replace missing tooth.
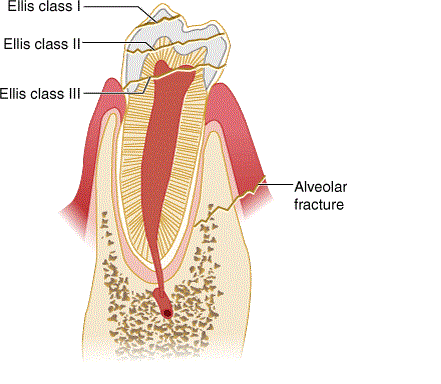

Ellis Classification
-
Used to describe type of fracture, what tissues are affected, and where the fracture is located on the tooth.
-
Class I: fracture of the crown that only involves the enamel. Damaged teeth are usually nontender, have a rough edge, and don't have a visible color change.
-
Class II: fracture of the enamel and dentin without pulp exposure; tender to the touch and to air exposure, with the possibility of a yellow layer of detin visible upon examination.
-
Class III: fracture of the crown and dentin with pulp exposure; tender witha visible area of pink, red, or blood at the center of the tooth.
-
Class IV: traumatized tooth with or without loss of tooth structure; non-vital (blood and/or nerve supply has been disrupted)
-
Class V: luxation; tooth dislocates from the alveolus; tooth loss can occur.
-
Class VI: avulsion; complete separation of a tooth from its alveolus; fracture of the root with or without loss of crown structure.
-
Class VII: displacement of a tooth without the fracture of crown or root.
-
Class VIII: Fracture of the crown en masse and its replacement.
-
Class IX: fracture of deciduous (baby) teeth
-
Potential Pathologies
(http://consumedandjudged.blogspot.com/2012/02/classification-and-treatment-of.html) Retrieved Nov 13 2014
Abscessed Tooth
-
Infection of the tooth; caused by bacteria left behind by poor dental hygiene.
-
Symptoms - pain, fever, swelling, tooth sensitivity, swollen lymph nodes, bad smell/taste in the mouth.
-
Diagnosis - tapping on the tooth, x-rays performed by a dentist
-
Treatment - referral to a dentist; excision of the tooth, root canal, or antibiotics will be used to treat.
-
Prevention - good dental hygiene habits
-
Athlete can participate as tolerated.
(http://www.thehealthsuccesssite.com/abscessed-teeth.html)
Retrieved Nov 13 2014

("Ellis Classification" 2010)
Tooth Luxation
-
Displacement of the tooth, accompanied by a fracture of the labial bone, the palatial or the linguinal alveolar bones. Caused by direct trauma.
-
Symptoms - pain, bleeding, displacement of tooth, swelling, laxity.
-
Diagnosis - visual observation
-
Treatment - immediate referral to dentist
-
Prevention - mouth guards and facial protection such as masks or cages
-
Athlete should rest a few days prior to return to play, then may participate as tolerated.
precomp&title=&Language=en&bone=CMF&segment=Dental)
Retrieved Nov 13 2014

Tooth Intrusion
-
Tooth is partially displaced upwards into the gums ("jammed"), caused by direct trauma.
-
Symptoms - pain, shorter appearance of tooth, swelling of gums, possible bleeding, sensitivity
-
Diagnosis - visual examination
-
Treatment - immediate referral to dentist
-
Prevention - mouth guards and facial protection such as masks or cages
-
Athlete should rest a few days prior to return to play, then may participate as tolerated.
(http://www.thenextdds.com/clinicalimages.aspx?catid=620&id=4294971395&y=2)
Retrieved Nov 13 2014

(Starkey 2010)
(Maanika 2013)